The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electronsSince the orbitals around an atom are defined in terms of a probability distribution in quantum mechanics and do not have fixed boundaries determining where an atom. A number of compounds containing Xe-C bonds are known.

Electron Configuration For Ti Ti3 And Ti4 Titanium And Titanium I Electron Configuration Electrons Chemical Bond
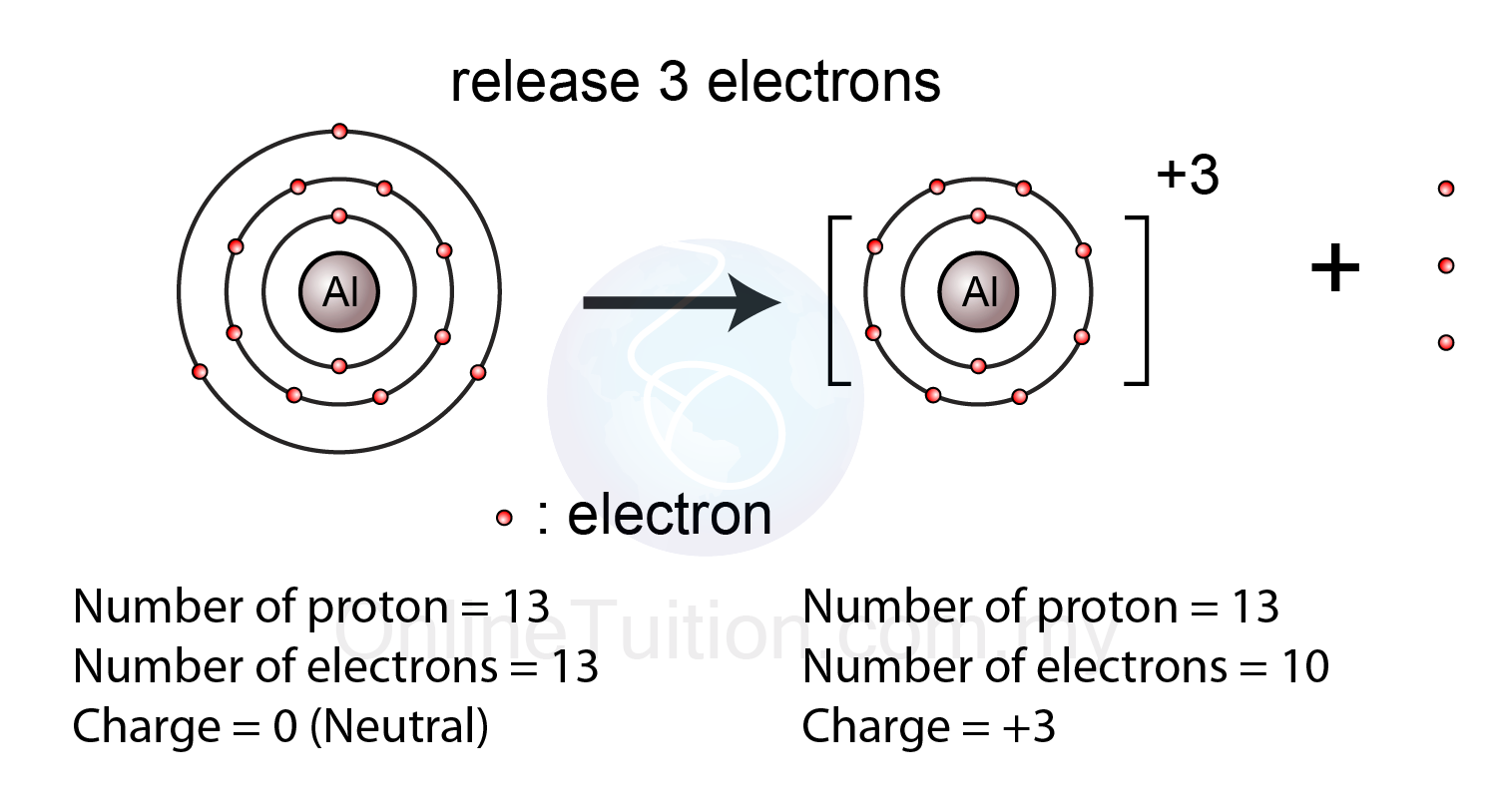
The most stable ion that aluminum forms is Al3 This ion has the same electronic configuration as NEON.

Atomic cations with 3 electrons.
The same dynamic is responsible for the steady increase in size observed as we go down.
Neutrons are relatively heavy particles with no charge and a mass of 10087 amu.
One other note on writing electron configurations.
Cations have more protons than electrons and so have a net positive charge.
Every atom in its ground state is uncharged.
Electrons are light particles with a charge of 1 and a mass of 000055 amu.
Anions are generally larger than the parent molecule or atom because the excess electrons repel each other and add to the physical size of the electron.
Ions are atoms with.
The f-orbital electrons are packed in in such a manner that it causes the atomic radius of gold to be actually SMALLER than the atomic radius of silver -- not by much but it is smaller.
It has according to its atomic number the same number of protons and electrons.
Electrons are rather labile however and an atom will often gain or lose them depending on its electronegativity.
For example sodium only has one electron in its outermost shell.
Zwitterions are neutral and have both positive and negative charges at different locations throughout the molecule.
The elements have very similar properties.
Negative ions are formed by gaining electrons and are called anions.
Atomic radii reported in units of picometers pm.
If the kinetic energy of the noble gas cations is high enough some of the metal atoms on the cathode will be dislodged producing an atomic cloud of metal in the gaseous phase.
Protons and Electrons in Polyatomic Ions When you are working with polyatomic ions ions consisting of groups of atoms the number of electrons is greater than the sum of the atomic numbers of the atoms for an anion and less than this value for a cation.
CATIONS positive ions have empty valence shells.
The negative charge of an electron is equal and opposite to charged protons considered positive by convention.
The net charge of an ion is non-zero due to its total number of electrons being unequal to its total number of protons.
The OH distance bond length is 957 picometres 957 10 11 metres or 377 10 9 inches.
Based on their VALENCE ELECTRONS.
Positive ions are formed by losing electrons and are called cations.
A normal atom has a neutral charge with equal numbers of positive and negative particles.
A smaller radius means more force from the nucleus on the outer electrons so silver wins in the conductivity contest.
Properties of Monatomic Ions The electrons in the outermost shell the ones with the highest value of n are the most energetic and are the ones which are exposed to other atoms.
While K and Ba2 are monoatomic ions NH4 and PO4 3- are POLYATOMIC ions.
Gaining electrons can yield negative species called anions.
The number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number Z and is the property that defines an atoms elemental identity.
Iron has 26 electrons so its normal electron configuration would be.
Because the number of electrons does not equal the number of protons each ion has a net charge.
Loss of electrons can lead to the formation of positive-charged species called cations.
Because electrons orbit around atomic nuclei they are the subatomic particles that affect chemical reactions.
Structurally they together with helium have in common an outer s.
Data taken from John Emsley The Elements 3rd editionOxford.
Fe 3 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 5.
The atomic number of an element also called a proton number tells you the number of protons or positive particles in an atom.
This shell is known as the valence shellThe inner core electrons inner shell do not usually play a role in chemical bonding.
They are all shiny silvery-white somewhat reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure.
Elements with similar properties generally have similar outer shell configurations.
Fe 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6.
As the electrons migrate toward the cathode they collide with the noble gas atoms and ionize them.
Cations and Anions form from Neutral Atoms.
The charge of the electron is considered negative by convention.
An example of.
These charged noble gas atoms collide with the cathode.
They are SMALLER than their neutral ATOM.
Ionic compounds exist as crystal lattice which is a network of anions and cations held together by electrostatic forces.
An ion ˈ aɪ ɒ n-ən is a particle atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
Description Build an atom out of protons neutrons and electrons and see how the element charge and mass change.
BUT the size of one ion compared to the next is the same pattern as.
We use the term FORMULA.
The driving force for such gain or loss of electrons is the.
Chemistry is essentially the study of electron transfer between atoms and molecules.
When we make a 3 ion for Iron we need to take the electrons from the outermost shell first so that would be the 4s shell NOT the 3d shell.
That means an atom with a neutral charge is one where the number of electrons is equal to the atomic number.
These compounds are salts of cations containing xenon2 coordinated to carbon and include cations such as C 6 F 5Xe and m-CF 3 C 6 H 4Xe.
Sample Learning Goals Use the number of protons neutrons and electrons to draw a model of the atom identify the element and determine the mass and charge.
Even though cesium has a nuclear charge of 55 it has 54 electrons in its filled 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 shells abbreviated as Xe5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 which effectively neutralize most of the 55 positive charges in the nucleus.
Then play a game to test your ideas.
Because an oxygen atom has a greater electronegativity than a hydrogen atom the OH bonds in the water molecule are polar with the oxygen bearing a partial negative charge δ and the hydrogens having a partial positive charge δ.
-determined the atomic number of elements and arranged the.
These include HCN and CH 3 3 CCN which interact with XeF to form the HCNXeF and CH 3 3 CCNXeF cations respectively.
The Sc 3 ion contains 21 protons and 18 electrons.
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group 2 of the periodic tableThey are beryllium Be magnesium Mg calcium Ca strontium Sr barium Ba and radium Ra.

Difference Between Atomic Radius And Ionic Radius Definition Calculation Trends In The Periodic Table Ionic Radius Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Study Guide

A Flow Chart Showing An Example Of Scaffolding In The Chemistry Classroom A Blog Post With Examples Chemistry Lessons Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Classroom

Bio Is Life Biochemistry Barron S Ap Biology Workbook 5th Science Notes Nursing School Notes Medical School Studying

This Google Slides Digital And Printable Science Lesson Includes Two Warm Ups Slide Distance Learning Interactive Science Notebook Learning Google Classroom

Electron Configuration For Co Co2 And Co3 Cobalt And Cobalt Ions Electron Configuration Electrons Chemical Bond

Educational Infographics And Homework Dates At The Coffee Shop Doodles In The Membrane Video Science Classroom Educational Videos Educational Illustration

Students Will Be Able To Identify Valence Electrons Determine Ions Formed And Explain The R Physical Science Lessons Chemistry Worksheets Chemistry Classroom

Anion Common Anions Their Names Formulas And The Elements They Are Derived From Physical Science Names Fluoride

Master The Periodic Trends Like Atomic Radius Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity With Thi Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Basics Study Chemistry











No comments:
Post a Comment